Generative Text AI
Generative Text AI has the potential to revolutionize the way we search and understand vast amounts of documents, such as books, articles, and research papers. With the ability to analyze and comprehend text on a massive scale, generative text AI can help us uncover insights and patterns that would be impossible to discover manually.
This technology can also assist with information retrieval by identifying relevant documents based on a user’s query. By analyzing the user’s search terms and the content of available documents, generative text AI can generate a list of relevant documents that are likely to contain the information the user is looking for.
Another area where generative text AI will have a significant impact is in natural language processing. This technology can help us better understand complex language and decipher meaning from context. This is very powerful because it allows us to analyze and understand text in a way that is similar to how humans do.
ChatGPT
ChatGPT provides evidence that Generative Text AI will transform how we operate in various aspects of our lives. ChatGPT has been very popular recently and it has actually attracted developers and companies to dabble into OpenAI APIs, the maker of ChatGPT. OpenAI provides public access to the models they use for ChatGPT via APIs. OpenAI APIs available in their website → OpenAI API.
Tech and Marketing companies are already using ChatGPT to improve productivity since it is capable of solving code problems, writing marketing copy, and even generating code. ChatGPT is also capable of generating code for a variety of programming languages, including Python, JavaScript, and Java. Let’s talk about this deeper in a different blog post!
Accessibility of AI
Open APIs allow access to the GPT-3 models, the LLM ChatGPT uses. Developers and companies have already built/integrated their products to power their search → GPT-3 powers the next generation of apps. GPT-3 have different flavors as indicated in their website → OpenAI GPT-3 Models.
A lot of developers also have developed tools to make it easier to use OpenAI APIs. I will discuss some of the tools I have discovered in this blog post. Some examples of tools you can use are LangChain and llama_index.
LangChain
Based on my research, using OpenAI APIs alone still needs some engineering work to use with existing data. One of the popular technologies is LangChain.
What is LangChain?
Large language models (LLMs) are emerging as a transformative technology, enabling developers to build applications that they previously could not. But using these LLMs in isolation is often not enough to create a truly powerful app - the real power comes when you can combine them with other sources of computation or knowledge. — source: LangChain website
LlamaIndex
Another technology which I discovered just recently is llama_index. Check out this article of my former boss Sau Sheong -> Prompt Engineering with LlamaIndex and OpenAI GPT-3 where I discovered llama_index.
LlamaIndex (formerly GPT Index) is a project that provides a central interface to connect your LLM’s with external data. LlamaIndex ( formerly GPT Index) is a simple, flexible interface between your external data and LLMs. It provides the following tools in an easy-to-use fashion.
LlamaIndex is easy to use and satisfies a common use case of using your own data and harness the power of GPT-3 for NLP and question-answering. LLamaIndex also uses LangChain as part of its tooling.
For this example, you can use Google Colab or a Jupyter Notebook. I used Google Colab to run the jupyter notebook for this example. You can also run a python script in your local machine if this is more convenient or easier for you.
Trying out llama_index
Here is an example of how to use llama_index. This is the basic example code provided in their documentation.
import os
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = ''
from llama_index import GPTSimpleVectorIndex, SimpleDirectoryReader
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader('/data').load_data()
index = GPTSimpleVectorIndex.from_documents(documents)
# save to disk
index.save_to_disk('index.json')
# load from disk
index = GPTSimpleVectorIndex.load_from_disk('index.json')
response = index.query("Question?")
print(response)The code does the ff.
- Configure your “OPENAI API KEY” environment variable. You need to get your API key from OpenAI. You can get it from here → OpenAI API.
- Loads a set of documents from the “/data” directory and creates an index of those documents. This is where you upload your PDFs you want to index and make searchable.
- Saves the index to a file named “index.json”.
- Loads the index from the “index.json” file.
- Queries the index with a question (represented by the string “Question?”) using the “query” method of the “GPTSimpleVectorIndex” class.
- Prints the response returned by the index query.
The default LLM used for this code is text text-davinci-003. For embeddings, it is using Ada.
text-davinci-003 is expensive so I researched on how to configure to use a cheaper model. I found out that gpt-3.5-turbo is a cheaper alternative.Unfortunately, for embeddings, Ada cannot be changed to use a cheaper model.
Here is a reference on how to change the LLMPredictor llama_index uses.
Modified code using gpt3-turbo and used the new way to initialize the LLMPredictor.
You can check out the full source code in this colab notebook I shared as a Github gist. → llama_index.ipynb
If you’d like to experiment on a more powerful model, you can try text-davinci-003 but it would be more expensive. It can give you better results. Reference → OpenAI GPT-3 Models. I used gpt-3.5-turbo for this example since it is 10x cheaper. You can check out the models pricing here → OpenAI Pricing.
import os
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = ''
from llama_index import LLMPredictor, GPTSimpleVectorIndex, PromptHelper, ServiceContext, SimpleDirectoryReader
from langchain import OpenAI
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from pathlib import Path
# set maximum input size
max_input_size = 4096
# set number of output tokens
num_output = 256
# set maximum chunk overlap
max_chunk_overlap = 20
# set temperature - less is more conservative, more is more creative
temperature = 0
# define LLM, you can try text-davinci-003 also but it would be more expensive. But it can give you better restults
# Reference https://platform.openai.com/docs/models
model_name = 'gpt-3.5-turbo'
llm_predictor = LLMPredictor(llm=ChatOpenAI(temperature=temperature, model_name="gpt-3.5-turbo", max_tokens=num_output))
prompt_helper = PromptHelper(max_input_size, num_output, max_chunk_overlap)
service_context = ServiceContext.from_defaults(llm_predictor=llm_predictor, prompt_helper=prompt_helper)
indexFile = 'index.json'
# START indexing part - comment this block if you alrady have the index saved to disk
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader('data').load_data()
index = GPTSimpleVectorIndex.from_documents(
documents, service_context=service_context
)
index.save_to_disk(indexFile)
# END indexing part
# load from disk
index = GPTSimpleVectorIndex.load_from_disk(indexFile)
# query the index
response = index.query("Which companies did Melvin work in the Philippines?", service_context=service_context)
# print token usage from the previous query
print(llm_predictor.last_token_usage)
# print the response of Open AI to the query
print(response)Running the example
Before running the example, you need to upload PDFs to the directory(“/data”) For this example, I uploaded my downloaded resme from LinkedIn. The code will automatically index all PDFs in the /data directory. This, I think, is one of the advantages of using llama_index. It does some convenience features which you don’t really need to worry about.
You can do the indexing once only so it won’t cost you OpenAPI Embedding API calls. You only enable this if you want to re-create the index of the documents.
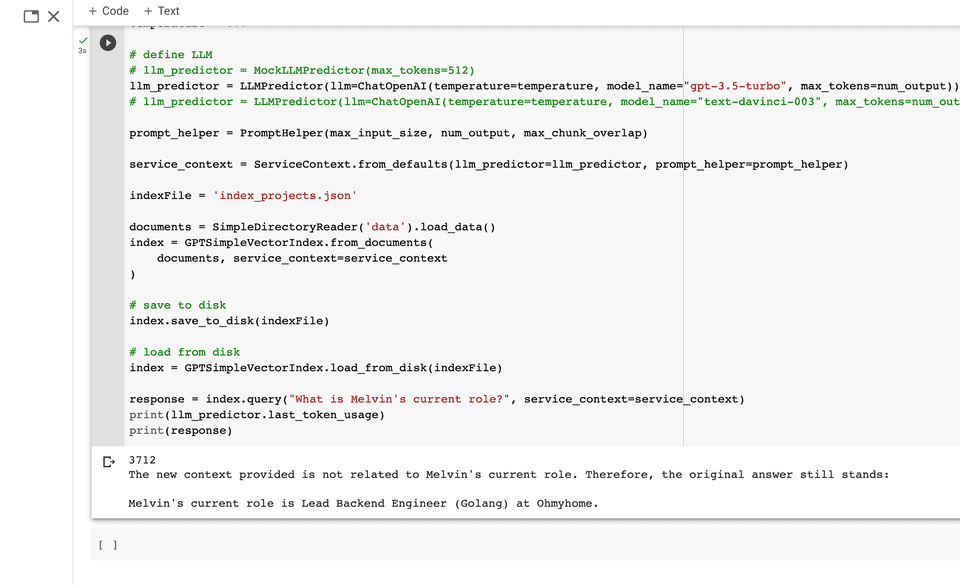
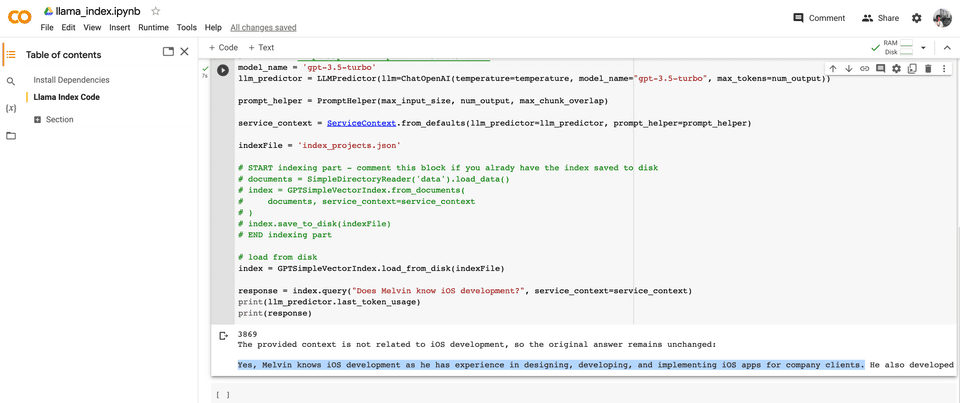
Here are some results of several runs.
- Question: What is Melvin’s current role?
- Answer: Melvin’s current role is Lead Backend Engineer (Golang) at Ohmyhome
- Question: Does Melvin know iOS development?
- Answer: Yes, Melvin knows iOS development as he has experience in designing, developing, and implementing iOS apps for company clients.
These are examples demonstrating how to use the llama_index tool with OpenAI. These can be powerful tools to develop powerful applications such as question answering, chatbots, and agents. It can help in discovery of information in documents and other sources. LlamaIndex also supports other file formats such as images, data from websites, csv, and more. Imagine the possibilities of using this tool in your applications.
For our use case, we are thinking of using OpenAI to answer questions about our services and products. We can also use it to answer questions about our company. This can be a powerful tool to help our customers and prospects.
Querying unstructured data is a challenge so we are also exploring the use of using OpenAI to help query our data and provide answers to our customers and prospects.
You can check out the full source code in this colab notebook I shared as a Github gist. → llama_index.ipynb
I hope this article helps you in your journey to develop your own applications with Open AI. I will find time to write more articles about Open AI and how to use it in your applications. You can reach me in my social media accounts below.
If you’d like to show your support and appreciation for my work, please consider buying me a coffee. Your support means a lot to me and will motivate me to continue creating content that you love. Thank you for considering to support my work!
Cheers!
Melvin Dave
You can reach me in my social media accounts below.