It’s pretty straighforward to convert a Docker compose file to a Kubernetes deployment. I used the kompose tool to do the conversion. Kompose is an official Kubernetes project. https://github.com/kubernetes/kompose
First step is to download kompose. Here is the command to install in a Mac. For other operating systems, check out the kompose website.
curl -L https://github.com/kubernetes/kompose/releases/download/v1.11.0/kompose-darwin-amd64 -o kompose
chmod +x kompose
sudo mv ./kompose /usr/local/bin/komposeHere is the docker compose file which I needed to convert.
docker-compose.yml (MongoDB)
version: '3'
services:
mongodb:
image: mongo
ports:
- "27017:27017"
volumes:
- "mongodata:/data/db"
networks:
- network1
volumes:
mongodata:
networks:
network1:Here is the very simple command I used!
kompose convert -f docker-compose.yamlIt will create 3 files
-
mongodata-persistentvolumeclaim.yaml - this is the configuration which creates the peristent volume to be used by the MongoDB container
apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolumeClaim metadata: creationTimestamp: null labels: io.kompose.service: mongodata name: mongodata spec: accessModes: -
ReadWriteOnce resources: requests: storage: 100Mi status: {}
-
mongodb-deployment.yaml - this is the deployment configuration which describes the deployment - which container to create and how many replicas, port info, volume links, etc.
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1 kind: Deployment metadata: annotations: kompose.cmd: kompose convert -f docker-compose.yml kompose.version: 1.11.0 (39ad614) creationTimestamp: null labels: io.kompose.service: mongodb name: mongodb spec: replicas: 1 strategy: type: Recreate template: metadata: creationTimestamp: null labels: io.kompose.service: mongodb spec: containers: - image: mongo name: mongodb ports: - containerPort: 27017 resources: {} volumeMounts: - mountPath: /data/db name: mongodata restartPolicy: Always volumes: - name: mongodata persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: mongodata status: {} -
mongodb-service.yaml - this config describes the service to be created
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: annotations: kompose.cmd: kompose convert -f docker-compose.yml kompose.version: 1.11.0 (39ad614) creationTimestamp: null labels: io.kompose.service: mongodb name: mongodb spec: ports: -
name: “27017” port: 27017 targetPort: 27017 selector: io.kompose.service: mongodb status: loadBalancer: {}
All of these files can also be found in my github repo. https://github.com/donvito/learngo/tree/master/mongo-microservice/mongodb
Once the configuration has been converted, you can now use these to create the service in the Kubernetes cluster. I am using Minikube since I am not able to make it work with Docker CE with Kubernetes support. Not sure if it’s because I am using the Edge version. Anyway, to keep things simple, I just started minikube in my laptop and switched the kubectl context to use minikube.
To learn how to install and run Minikube, check out the documentation https://kubernetes.io/docs/getting-started-guides/minikube/
Once you have your minikube cluster up, just create the deployment.
kubectl create -f mongodata-persistentvolumeclaim.yaml
kubectl create -f mongodb-deployment.yaml
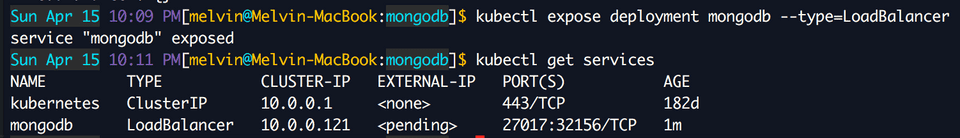
kubectl create -f mongodb-service.yamlOnce the service is up, you need to expose the deployment so you can access the MongoDB running in your Kubernetes cluster.
kubectl expose deployment mongodb --type=LoadBalancerTo get the IP address and port to connect to, just use this command. It will open up a browser and will show you which IP and port to connect to.
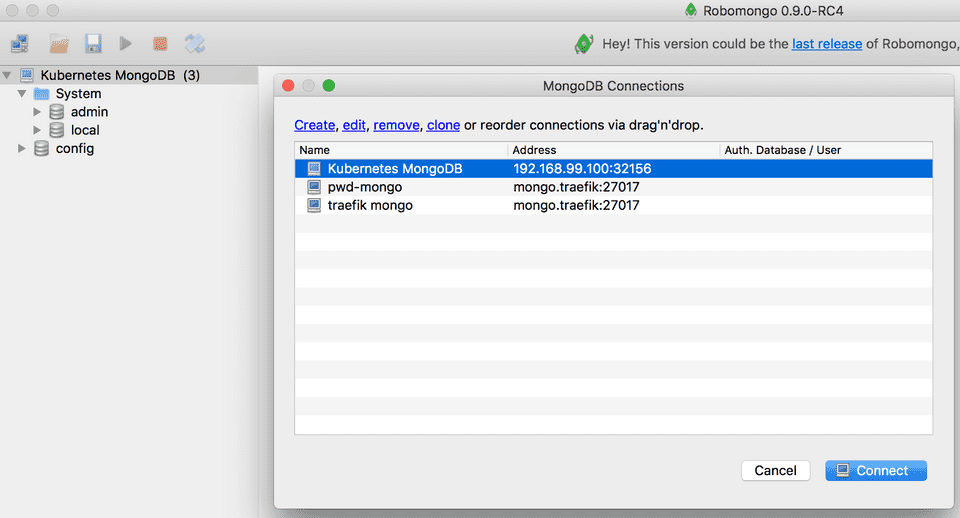
minikube service mongodbUse this IP and port to connect to MongoDB. I am using RoboMongo to connect.
That’s it! We now have a converted Docker compose file of a MongoDB service and we were able to run it in a Kubernetes cluster.
Shameless plug! If you like this blog post, please follow me in Twitter @donvito. I tweet about Docker, Kubernetes, GoLang, Cloud, DevOps, Agile and Startups. Would love to connect in GitHub and LinkedIn as well!